Carpal Tunnel Release
What is Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery?
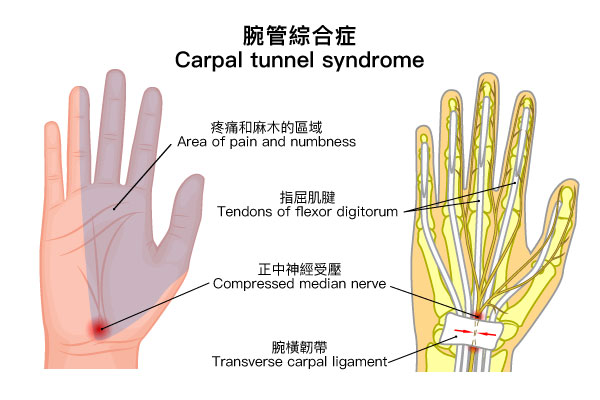
Carpal tunnel release surgery is a surgical procedure designed to treat carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). CTS is a common hand condition characterized by pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the fingers, thumb, palm, and forearm.
Function of the Carpal Tunnel
The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway located on the palmar side of the wrist, formed by the carpal bones and the flexor retinaculum. The tunnel contains several structures, including the median nerve and multiple flexor tendons.
The primary function of the carpal tunnel is to provide a route for the flexor tendons and the median nerve to pass through. The median nerve is responsible for sensory and motor functions in the hand, while the flexor tendons facilitate the bending of the fingers and wrist.
Who is at Risk for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal tunnel syndrome can affect individuals of any age and gender; however, certain populations are at a higher risk. Risk factors for developing CTS include:
-
Repetitive Hand Use: Engaging in prolonged repetitive hand movements or postures, particularly those requiring significant finger and wrist motion, such as typing, assembly work, or sewing, increases the risk of developing CTS.
-
Pressure and Vibration: Long-term exposure to pressure and vibration in the workplace, such as using vibrating tools or machinery, may elevate the risk of CTS.
-
Gender: Women are more likely to develop CTS compared to men, potentially due to anatomical differences and hormonal changes.
-
Age: The risk of CTS increases with age, likely due to changes in tissue structure and the development of chronic conditions.
-
Genetic Factors: Certain hereditary factors may heighten the risk of CTS, with individuals having a family history of the condition being more susceptible.
-
Other Health Issues: Conditions such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, arthritis, and obesity are associated with an increased incidence of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Treatment for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Treatment options for carpal tunnel syndrome can be categorized into non-surgical and surgical approaches, depending on the severity of the condition and individual patient needs. Common treatment options include:
Surgical Treatment
If non-surgical methods fail to alleviate symptoms or if the condition is severe, a doctor may recommend surgical intervention known as carpal tunnel release surgery.
Open Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery:
-
The surgery can be performed under monitored anesthesia care or general anesthesia.
-
An incision is made on the palm of the hand.
-
The ligament causing compression of the median nerve is cut to relieve pressure.
-
If necessary, surrounding tissues may also be excised.
-
The incision is then sutured closed.
-
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery:
-
This minimally invasive technique utilizes an endoscope for the procedure.
-
The surgeon makes a small incision and inserts the endoscope along with other surgical instruments.
-
The flexor retinaculum is cut from the bottom of the carpal tunnel to achieve release.
-
Both surgical techniques aim to alleviate symptoms by relieving pressure on the median nerve, allowing for improved function and reduced discomfort in the affected hand.
Preparation
-
Fasting Requirements: Patients are typically required to fast for 6 hours prior to surgery, meaning no food intake during this period. A small amount of plain water is permitted until 2 hours before the procedure.
-
Preoperative Medications: Please take any prescribed medications as directed. If you are currently taking blood-thinning medications, such as Aspirin, Warfarin, Xarelto, or Pradaxa, or any herbal supplements, inform your doctor as soon as possible.
-
Informed Consent: The doctor will discuss the reasons for the procedure, the process involved, and any potential complications. After gaining a clear understanding, patients will be asked to sign the consent form.
Follow-up and recovery
-
Wrist Care: Rest your wrist and avoid bending it to minimize tendon inflammation and swelling.
-
Finger Activity: Regularly move your fingers and other upper limb joints to reduce swelling and enhance function.
-
Wound Care: Keep any wounds on your hand dry and clean. Avoid exposure to water. Stitches are typically removed 14 days after surgery.
-
Pain Management: If you experience pain at the wound site, take pain medication as directed by your healthcare provider.
-
Post-Anesthesia Care: After receiving anesthesia or sedatives, you may feel slightly dizzy. It is important to rest in bed and allow the effects of the medication to diminish before attempting to get up, which may take three to four hours.
-
Common Symptoms: Following surgery, you may encounter headaches, dizziness, nausea, or inflammation at the venipuncture site. These symptoms should resolve naturally within a few days.
-
Eating Instructions: Wait until the effects of anesthesia and sedatives have worn off before eating to avoid choking.
-
Restrictions: Refrain from consuming alcohol, operating heavy machinery, or driving on the day of surgery to prevent accidents. Additionally, do not sign any legal documents within 24 hours after the procedure.
-
Discharge: Patients will be able to leave once the effects of anesthesia have subsided but must be accompanied by an adult.
-
Rehabilitation Exercises: Follow your doctor’s or physical therapist’s recommendations for rehabilitation exercises. These are essential for restoring strength, flexibility, and function to your fingers. Engage in these exercises gradually and moderately.
-
When to Contact a Doctor: If you notice any pain, swelling, bleeding, infection, or other unusual symptoms in your fingers, please contact your doctor immediately.
Reference
Mayo Clinic. Carpal tunnel syndrome. Available at : https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/carpal-tunnel-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20355603

 3405 8288
3405 8288