Types of Haemorrhoids
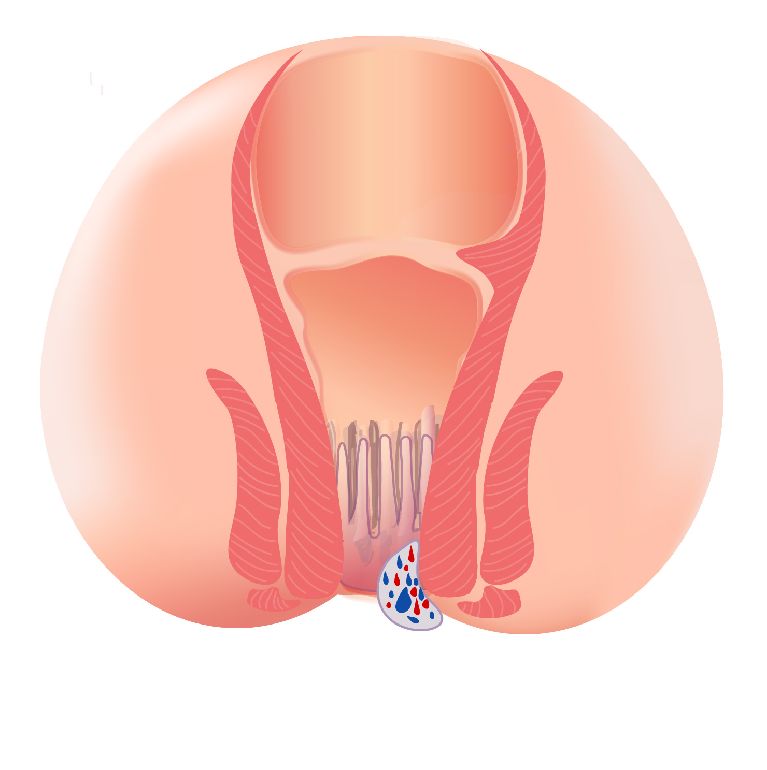
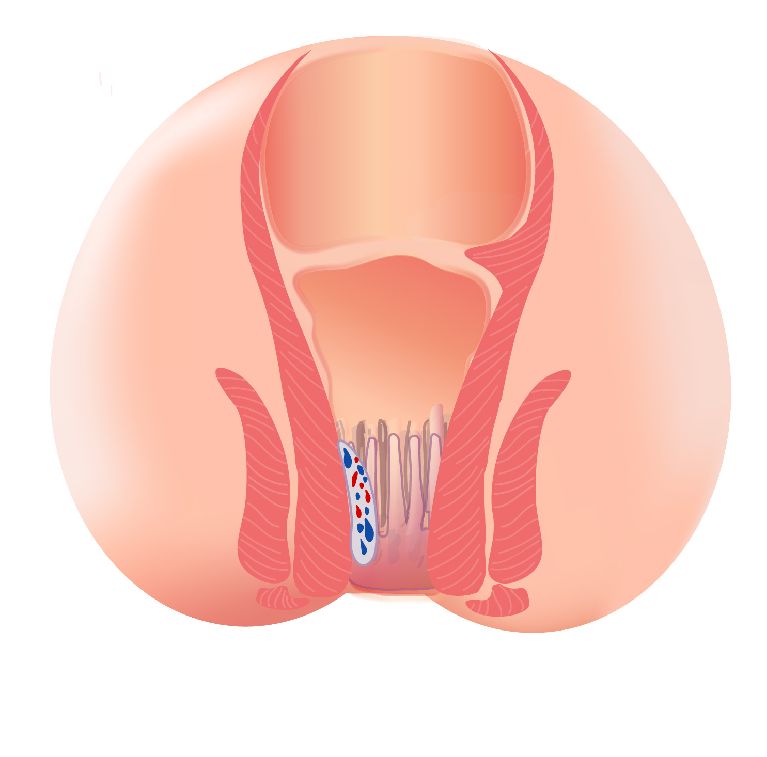
There are three types of haemorrhoids: Internal haemorrhoids, external haemorrhoids, and interno-external haemorrhoids. Signs and symptoms may be different between the first two types of haemorrhoids. Many patients may have both external and internal (mixed) haemorrhoids.
| External haemorrhoids | Internal haemorrhoids | Interno-external haemorrhoids |
 |
 |
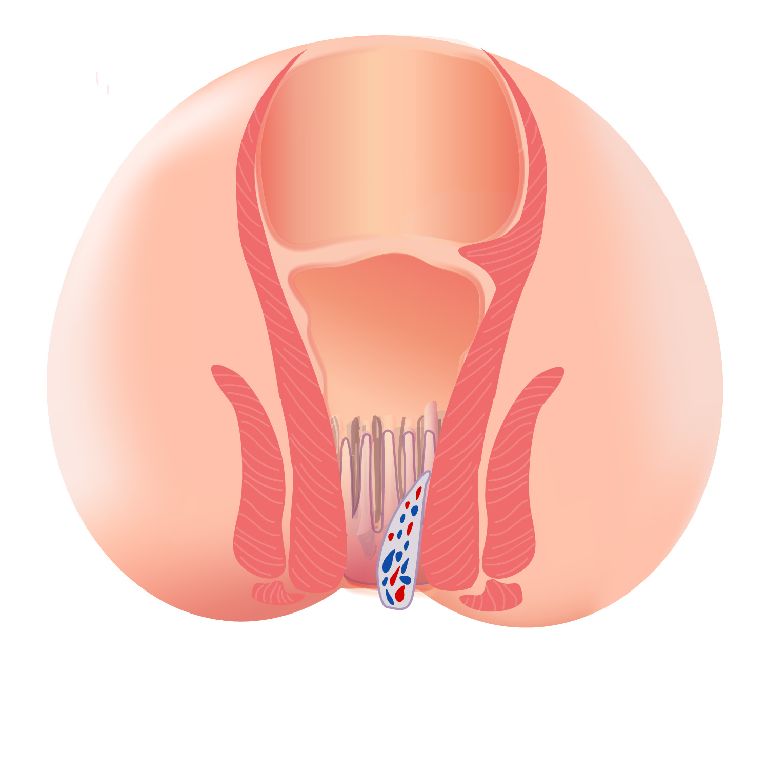 |
| Occur below the dentate line | Occur above the dentate line | Mixed haemorrhoids are formed both above and below the dentate line. |
| If there is thrombosis of external haemorrhoids, patients may feel sudden and severe pain. | Patients usually do not feel pain. | Patients can feel anal discomfort and pain. |
| When the haemorrhoid develops and the clot dissolves, leaving excess skin, it becomes itch or irritated around the anus. | Patients might notice painless anal bleeding during or after defecation. | There may be discharge ,mucus, discomfort or itchiness around the anus. |
Causes
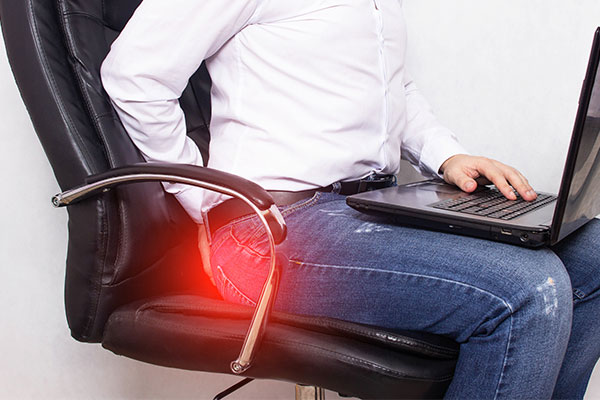
The exact causes of haemorrhoids are not confirmed. Chronic constipation, chronic straining, the lack of dietary fibre from fruits and vegetables in one's diet, prolonged sitting, pregnancy, old age and genetic hereditary may contribute to the formation of haemorrhoids.
Diagnosis
When patients find blood on the toilet paper after passing the stool, see a lump hanging down outside the anus, or may feel pain, they should seek medical advice at the earliest. Patients may need to have colonoscopy which can identify sites of bleeding and detect the colonic problems.
Treatment
Treatments include conservative treatments and surgery, depending on different severity levels. For early haemorrhoids, doctors will recommend conservative treatments, such as having a high-fibre diet and taking some medications or rubber band ligation. The rubber band ligation restricts blood flow, eventually causing the haemorrhoid to shrivel up and fall off. The purpose is to stop the haemorrhoid becoming worse and ease the symptoms.
Haemorrhoid ligation or Open diathermy haemorrhoidectomy and stapled haemorrhoidectomy are suitable for serious haemorrhoids. Open diathermy haemorrhoidectomy uses diathermy to excise the haemorrhoid. Wound pain at anus is relatively more intense. As the wound is exposed, cleaning of wound after each bowel movement is advised. Stapled haemorrhoidectomy can excise and fix the anal mucous membrane. Patient may experience short-term and slight discomfort after the surgery. However, no special caring is needed as the wound is not exposed.
Prevention
The best way of preventing haemorrhoid is to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Citizens are highly advised eating abundant vegetables, fruits and cereals, drinking sufficient fluid to soften the stools and to maintain a regular bowel habit. Avoiding straining during bowel movements is also very important. Regular exercise can promote blood circulation to reduce the chance of getting haemorrhoids. Besides, we suggest our citizens standing up and moving around after long periods of sitting which is harmful to our health.
*The above information is for reference only, please consult your doctor for detail.

 3405 8288
3405 8288
