Hand, Foot and Mouth Diseas

Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common disease in children. The usual peak season for HFMD in Hong Kong is from May to July and a smaller peak may also occur from October to December.
Symptoms
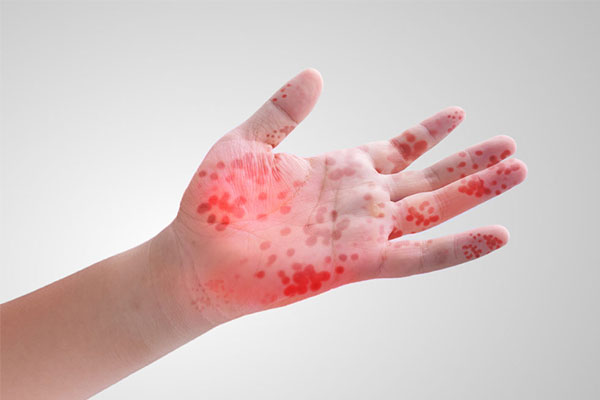
The disease usually begins with fever, poor appetite, tiredness and sore throat. One to two days after fever onset, painful sores may develop in the mouth. They begin as small red spots with blisters and then often become ulcers. They usually appear on the tongue, gum and inside of the cheeks. There may also be a skin rash that is non-itchy and sometimes accompanied by blisters. The rash usually appears on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet and may also appear on the buttocks and/or genitalia. A person with HFMD may not have symptoms, or may only have rash or mouth ulcers.
Enterovirus
The disease is mostly caused by enteroviruses such as coxsackieviruses and enterovirus 71 (EV71). HFMD caused by EV71 is more likely associated with severe complications (such as viral meningitis, encephalitis and poliomyelitis-like paralysis) and even death.
Mode of transmission
The disease mainly spreads by contact with an infected person’s nose or throat discharges, saliva, fluid from vesicles or stool, or after touching contaminated objects. The disease is most contagious during the first week of the illness and the viruses can be found in stool for weeks.
Diagnosis
Most patients can be diagnosed by observing the symptoms. And occasionally they need to take throat discharge or faecal sample to check for the presence of the virus.
Treatment
The disease is mostly self-limiting and resolves in 7 - 10 days. Sick children should stay away from school or gatherings till all vesicles have dried up to avoid spreading the disease. Patients should drink plenty of water and take adequate rest, and may receive symptomatic treatment to reduce fever and pain from oral ulcers.
If the infection is caused by EV71, the patient is advised to stay at home for two more weeks after recovery from the disease (i.e. fever and rash have subsided, and vesicles have dried and crusted).
Prevention
Good personal and environmental hygiene are the mainstay of prevention.
- Wash hands with liquid soap and water, rub for at least 20 seconds, then dry with a disposable paper towel or hand dryer. If hand washing facilities are not available, or when hands are not visibly soiled, hand hygiene with 70-80% alcohol-based hand rub is an effective alternative.
- Cover your mouth and nose with tissue paper when sneezing or coughing. Dispose of soiled tissue paper into a lidded rubbish bin, then wash hands thoroughly.
- Avoid close contact (such as kissing, hugging) with infected persons.
- Refrain from work or attending class at school, and seek medical advice if feeling unwell.
- Exclude infected persons from handling food and from providing care to children, elderly and immunocompromised people.
- Regularly clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces such as furniture, toys and commonly shared items. For metallic surface, disinfect with 70% alcohol.
- Avoid group activities when HFMD outbreak occurs in the school or institution. Besides, minimise staff movement and arrange the same group of staff to take care of the same group of children as far as possible.
*The above information is for reference only, please consult your doctor for detail.

 3405 8288
3405 8288
